
When a request arrives at a portal targeted to a portlet, the portlet container executes portlet code according to a phase model.
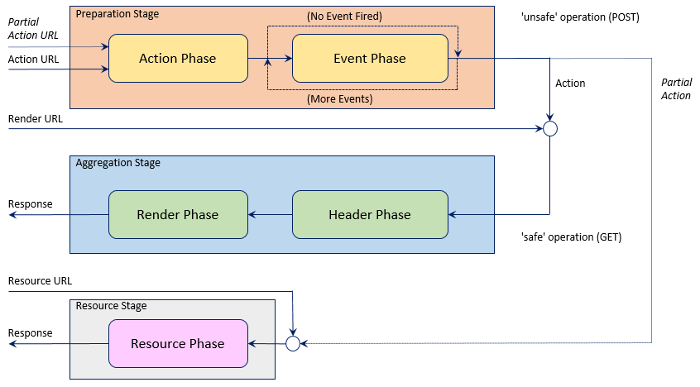
There are three processing stages containing five processing phases, defined as follows:
The portlet API allows creation of URLs that can be included into portlet markup in order to activate the portlet processing stages.
When a stage is triggered, the processing phases within that stage are executed.
The portlet container drives portlet phase execution by setting up the execution environment for each portlet and phase and calling the corresponding portlet lifecycle methods.
The portlet participates in the phase model by implementing the corresponding lifecycle methods and by using the portlet API to carry out the appropriate tasks.
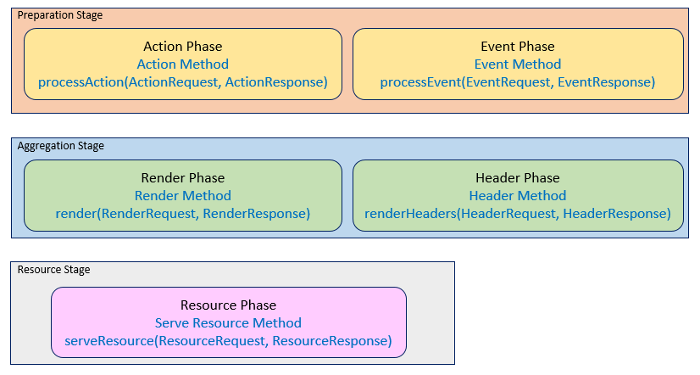
Each portlet phase has a corresponding lifecycle method. The portlet container executes the prrocessing phase by calling the portlet lifecycle method. Each phase is provided with specific request and response objects. Methods can implemented using the interfaces Portlet, ResourceServingPortlet, EventPortlet and HeaderPortlet. Portlets can be configured through annotation or using the portlet deployment descriptor.
Portlets can implement the lifecycle methods by extending the GenericPortlet class or by using the extended method annotations.
When the extended method annotations are used, portlet lifecycle methods can be arbitrary methods in java classes. The methods are identified by the portlet lifecycle method annotations and have relaxed method signature requirements as compared to interface methods. When the method annotations are used, portlets are implicitly configured if no data beyond that provided in the annotation is required. Additional configuration is possible through annotation or portlet deployment descriptor.