Deploying custom portlets in Jetspeed-2 is simple. Portlets are very similar to servlets.
They require a deployment descriptor, portlet.xml which goes in WEB-INF
and need to be packaged in a war-like format. You can find quite a few example portlet.xml files within the Jetspeed-2 source tree.
For starters take a look at the one under /portal/src/webapp/WEB-INF. In order to deploy a portlet, Jetspeed-2 requires the user
to follow those steps:
WEB-INF/deploy.
Jetspeed will take care of automatically deplying the portlet into the portlet registry and will also deploy the portlet
as a web application into the app server Jetspeed is deployed to.default-page.psml under jetspeed/WEB-INF/pages.
The id for the portlet fragment uses a unique combination of ${portlet.application.id}::${portlet.name}
where ${portlet.application.id} is the actual name of the war file (minus the ".war") that contains your portlet app and
${portlet.name} needs to be the value in the portlet name tags, <portlet-name>MyPortlet</portlet-name>.
Changes to the psml will be picked up automatically and you should now be able to view your portlet!
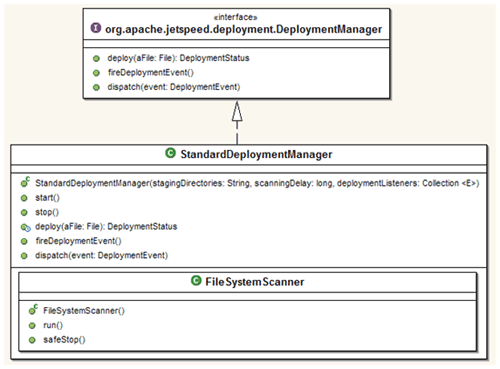
The component hierarchy below describes the assembly dependencies supporting Jetspeed-2 deployment functionality.
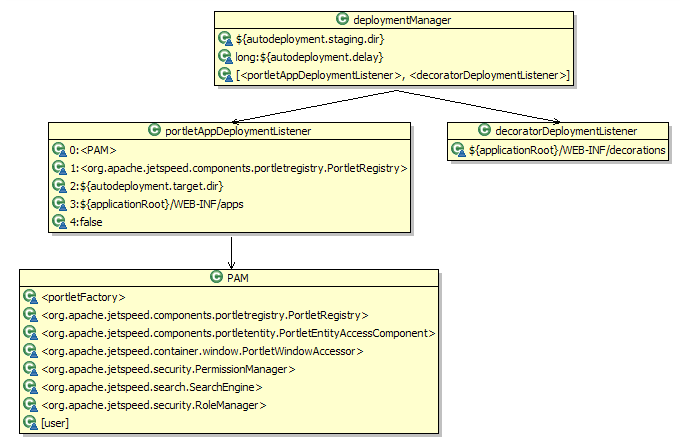
The DeploymentManager is configured with the properties specified in
WEB-INF/conf/jetspeed.properties:
autodeployment.staging.dir: The directory scanned for autodeployment.autodeployment.delay: The frequency of the deploy directory scanning.DeploymentManager is also configured with 2 types of DeploymentEventListener:
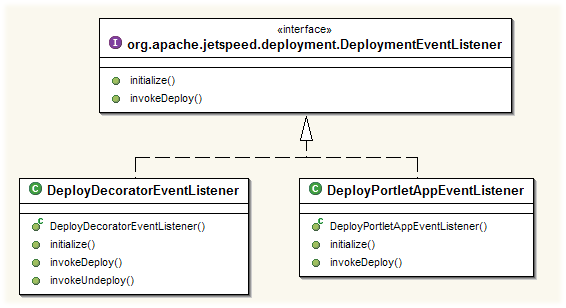
DeployPortletAppEventListener handles the hot deployment of portlet applications.DeployDecoratorEventListener: handles the hot deployment of decorators. See
guide to decorators for more information.
Jetspeed-2 provides a StandardDeploymentManager. The StandardDeploymentManager leverages
a FileSystemScanner to scan for new assets to deploy. It leverages Jetspeed-2
deploy tools to prepare portlet applications prior to deployment.